ACLSAdvanced Cardiovascular Life Support for Critical Care Situations
ACLS Arrest Algorithm: See on AHA's website

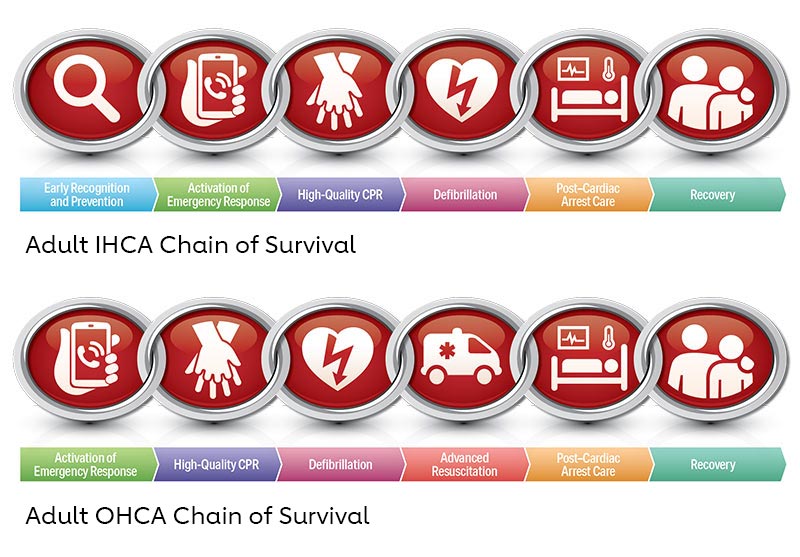
ACLS Arrest Circular Algorithm: See on AHA's website
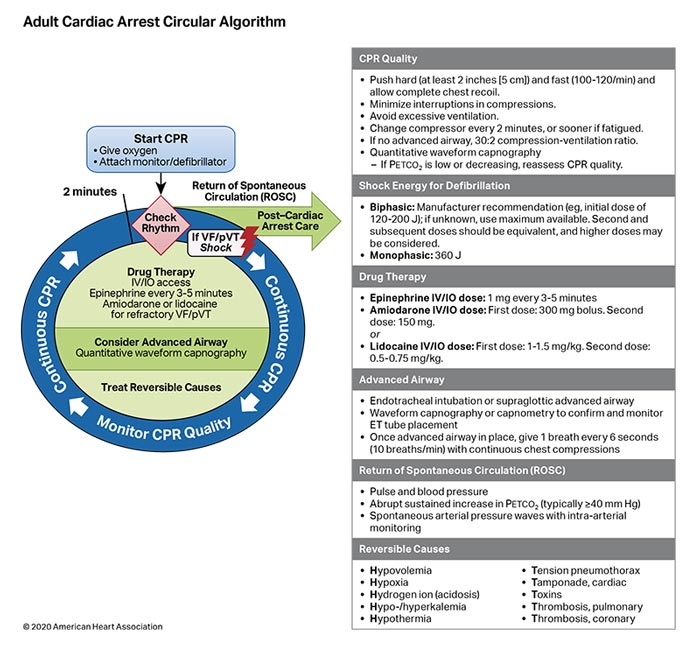
ACLS, Termination of Resuscitation: See on AHA's website
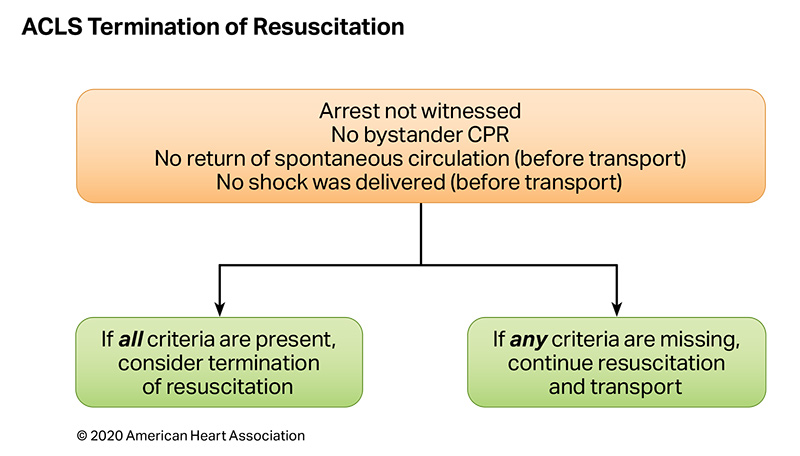
Chain of Survival: See on AHA's website
IHCA: In-Hospital Cardiac Arrest
OHCA: Out-of Hospital Cardiac Arrest
Advanced Cardiovascular Life Support (ACLS) is an essential set of interventions and algorithms designed to provide optimal care for patients experiencing life-threatening cardiac emergencies. Developed by the American Heart Association (AHA), ACLS guidelines provide healthcare professionals with the knowledge and skills necessary to manage cardiac arrest, stroke, and other critical conditions. In this blog, we will delve into the latest ACLS guidelines to understand the key components and interventions that can help improve patient outcomes in critical care situations.
- Management of Cardiac Arrest:
- BLS Survey:Assess the patient's responsiveness, activate the emergency response system, and initiate CPR if necessary.
- Rapid Defibrillation:Early defibrillation is critical for patients with shockable rhythms (ventricular fibrillation or pulseless ventricular tachycardia). Use an AED or manual defibrillator to deliver appropriate shocks.
- Airway Management:Establish and maintain a patent airway using advanced airway devices (endotracheal tube or supraglottic airway). Monitor oxygenation and ventilation closely.
- Medications:Administer medications such as epinephrine, vasopressin, amiodarone, or lidocaine as per the specific cardiac arrest algorithm.
- Acute Coronary Syndromes:
- Early Recognition:Promptly identify and evaluate patients with symptoms suggestive of acute coronary syndromes.
- Reperfusion Therapy:Administer fibrinolytic therapy or perform percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) as appropriate for STEMI patients within the recommended timeframes.
- Medications:Initiate antiplatelet therapy, anticoagulation, and other appropriate medications to manage acute coronary syndromes.
- Continuous ECG Monitoring:Monitor patients for arrhythmias and ischemic changes.
- Stroke Management:
- Rapid Assessment:Perform a focused neurological assessment to identify stroke symptoms and assess the time of symptom onset.
- Imaging and Evaluation:Conduct brain imaging to determine the type and cause of stroke. Assess eligibility for thrombolytic therapy.
- Blood Pressure Management:Maintain blood pressure within specific target ranges to ensure adequate cerebral perfusion.
- Airway and Breathing Management:Provide supplemental oxygen and ventilatory support as needed.
- Post-Cardiac Arrest Care:
- Targeted Temperature Management:Consider induced hypothermia or targeted temperature management for eligible patients.
- Hemodynamic Optimization: Maintainadequate oxygenation, ventilation, and blood pressure. Use vasoactive medications as necessary.
- Coronary Reperfusion:Evaluate the need for emergent coronary angiography and PCI in patients with suspected or confirmed acute coronary syndromes.
- Neurological Prognostication:Use validated tools to assess neurological function and determine appropriate care goals.
ACLS plays a critical role in managing life-threatening cardiac emergencies, acute coronary syndromes, and strokes. The latest guidelines provided by the American Heart Association (AHA) outline key interventions, including high-quality CPR, defibrillation, medication administration, and targeted therapies for optimal patient outcomes. By staying updated with ACLS guidelines and receiving proper training, healthcare professionals can effectively respond to critical care situations, ultimately improving survival rates and enhancing the quality of care provided to patients in need.
a project of alostmedic.com